Effects of Injection Molding Process on Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber Reinforced PBT/Microsphere Foam Materials
Engineering Plastic Application, one of plastics industry’s core journals, recently published Crerax’s research results titled “Effects of Injection Molding Process on Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber Reinforced PBT/Microsphere Foam Materials”. The research set out to achieve lightweight for glass fiber reinforced PBT using Crerax’s expandable microspheres and has demonstrated a wide range of applications of Crerax’s products in engineering plaPBT engineering plastics have the advantages of heat resistance, high strength, high insulation, low water absorption and low friction, etc., and are widely used in electronic appliances, automobile industry, office machinery and other industries. It is mainstream to achieve lightweight (lower density) and a lower production cost (reduce injection cycle time and consumption of materials) for injection molded parts through micro-foaming techniques. However, neither supercritical liquid foaming nor chemical foaming can achieve this goal without seriously affecting the mechanical properties or shooting up the production costs.
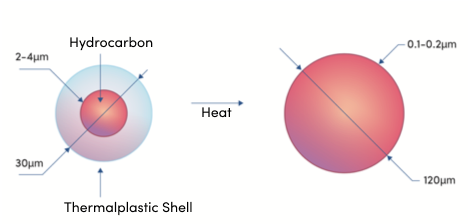
As a new foaming agent, Crerax’s patented expandable microspheres create stable-sized cells after heating, reducing density and increasing thermal insulation effect with minimal effects on mechanical properties of the foamed material. The research uses glass fiber reinforced PBT and Crerax microspheres during injection foaming and studies the how various process parameters (barrel temperature, injection pressure, dwell time, injection back pressure, and screw speed) affect the density, tensile properties, bending properties, tensile specific strength, bending specific strength, and other mechanical properties of the foamed material.
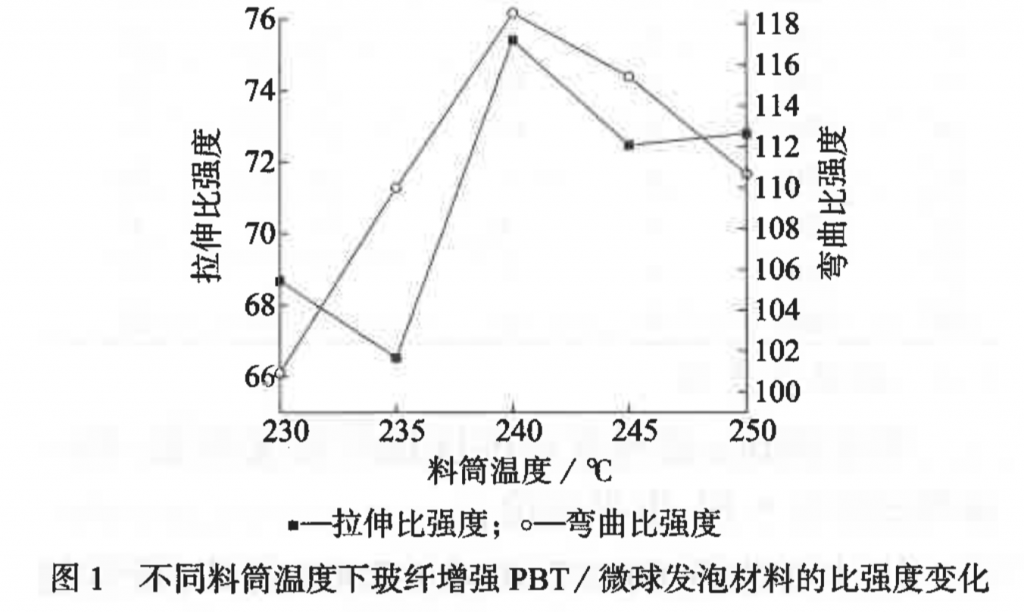
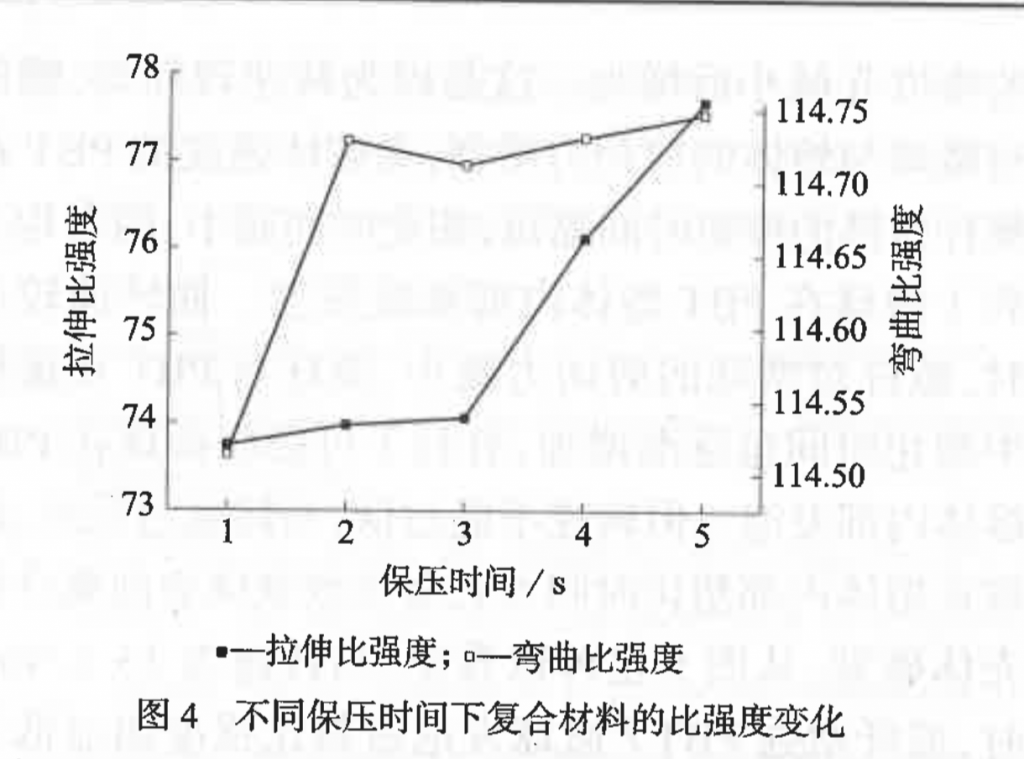
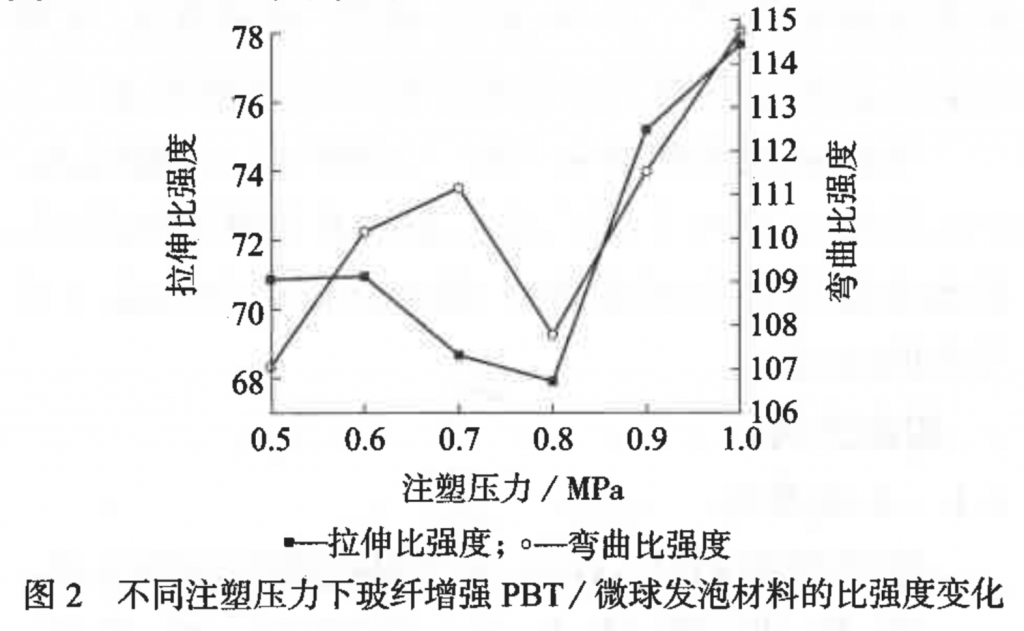
The increase of barrel temperature, injection pressure and dwell time is conducive to microsphere foaming, which reduces the density of glass fiber reinforced PBT / microsphere foamed materials, but the increase of barrel temperature will cause the tensile specific strength and bending specific strength to increase first and then decrease; the increase in injection pressure will first decrease and then increase the tensile specific strength, and cause the bending specific strength to fluctuate with an upward trend. The increase of dwell time will make both the tensile specific strength and the bending specific strength to increase.
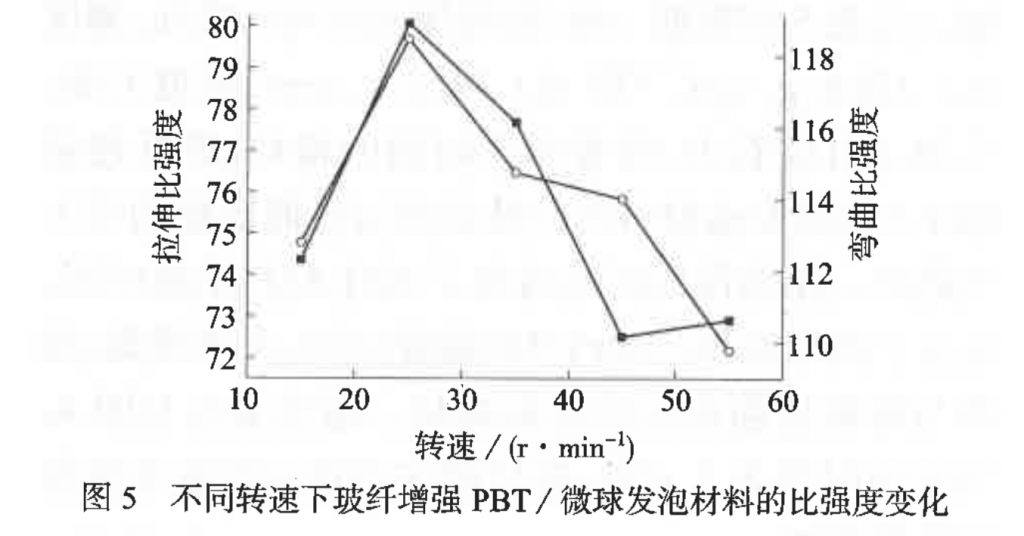
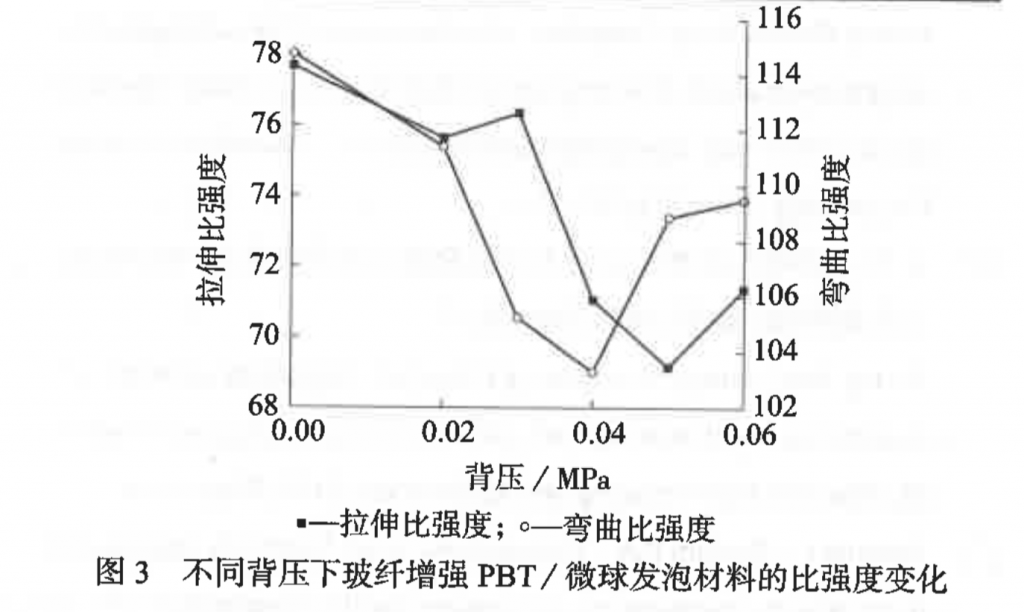
Bringing up the back pressure will increase the density of foamed materials. The tensile specific strength is at its highest level when back pressure is at 0, and will show a downward trend in fluctuation with the increase of back pressure, while the bending specific strength will first decrease and then increase. Increasing the screw speed will cause the density of the material to decrease first and then increase, and both specific strengths to increase and then decrease.
The research finds that the optimal process parameters for glass fiber reinforced PBT / microsphere foaming materials are as follows:
– barrel temperature: 240 °C
– injection pressure: 1.0 MPa
– back pressure: 0 MPa
– dwell time: 5 s
– screw speed: 25 r / min
Under the above parameters, the foamed materials can reach a density of 1.3472 g / cm3, a weight loss of 10.78%, a tensile specific strength increase of 6.14%, and a bending specific strength increase of 9.74%.

“Effects of Injection Molding Process on Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber Reinforced PBT/Microsphere Foam Materials”
Authors: Crerax Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Gao Liang, Zhang Chao, Zhu Naxin, Zhang Hengdi